INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY > Expansion Card, Bus Lines, & Ports- Expansion cards are circuit boards that provide more memoryor that control peripheral devices (for graphics, sound, video, networkinterface, wireless connection, etc.).
- Buses connect the expansion cards to ports.
- A port is a connecting socket or jack on the outside of thecomputer unit or device into which are plugged different kinds of cables thatconnect peripheral devices.
- Expansion Cards: If a computer uses closed architecture, noexpansion cards can be added; if thecomputer uses open architecture, expansion cards can be inserted in expansionslots inside the computer, connected to the motherboard.
- An expansion bus is not the same as the frontside bus:
- Frontside bus: The bus that connects the CPU within itselfand to main memory.
- Expansion bus: Buses that connect the CPU with expansionslots on the motherboard and thus via ports with peripheral devices.
- Types of expansion buses:
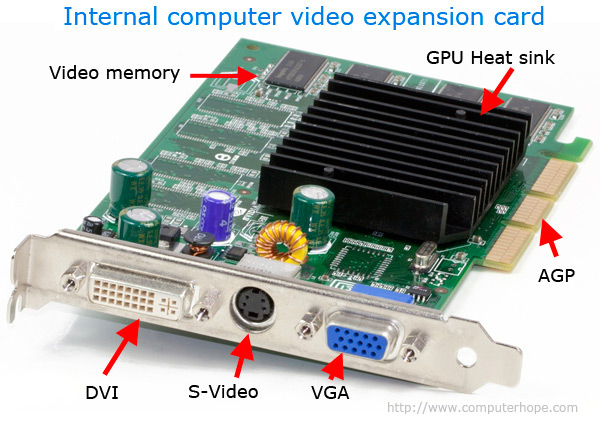
- PCI: High-speed bus that has been widely used to connect PCgraphics cards, sound cards, modems, and high-speed network cards.
- PCI Express: Doubles the speed of the original PCI bus .PCIe is the latest standard for expansion cards available on mainstreampersonal computers.
- Accelerated Graphics: Transmits data at twice the speed of aPCI bus and is designed to support video and 3-D graphics.
- Universal Serial Bus (USB): Does away with the need toinstall cards in expansion slots. USB devices can connect one to anotheroutside the system unit, and then the USB bus connects to the PCI bus on themotherboard.
- Firewire: Resembles the USB bus but is used for morespecialized purposes, such as to connect audio and video equipment to themotherboard.
Port There are many type of port that are available such as : - Serial port : Used to transmit data slowly over long distance
- Sends data sequentially, one bit at a time
- Used to connect older keyboards, mouse, monitors, dial-upmodems
- Parallel port : For transmitting data quickly over short distances
- Transmits 8 bytes simultaneously
- Connects printers, external disks, tape backups
- USB port : Universal Serial Bus high-speedhardware standard for interfacing peripheral devices, such as scanners andprinters, to computers without a need for special expansion cards or otherhardware modifications to the computer. USB is replacing many varieties ofserial and parallel ports.
- FireWire : Intended for multiple devices working with lots ofdata and requiring fast transmission speeds, such as DVD drives,digital video cameras, and gaming consoles.
- Ethernet: Supports anetwork standard for linking a wired local area network and connecting it to a DSL or a cable modem for high-speed Internet access.
- Graphics : Connects digital monitors and multimedia digitaldevices, such as TVs and DVD players.
- eSATA : ExternalSerial Advanced Technology Attachment; allows the attachment of an eSATA hard disk, which has fast data transmission speeds.
- Bluetooth : Connects devices that use short-range radio waves thattransmit up to 30 feet.
- IrDA :Transfers data via infrared light wavesbetween directly aligned devices, as between a smartphone and a desktopcomputer.
- HDMI : High-Definition Multimedia Interface; carries bothvideo and audio signals and is used for connecting HDTVs, DVD players, and gameconsoles to computers, laptops, and other devices.
- MIDI : Musical Instrument Digital Interface; used toconnect electronic musical instruments to a sound card that converts thesignals to digital instructions that can be saved or manipulated.
|
|
Some PCs have a mixture of PCI and PCI Express slots. If so, go with PCI Express when you have that option. AGP: This type of expansion slot was specifically designed to deal with graphics adapters. In fact, AGP stands for Accelerated Graphics Port. Older PCs may sport this expansion slot, but the best video cards use PCI Express.
Difference Between Expansion Slots And Ports List
Difference Between Expansion Slots And Ports Needed
Slots refer to connectors on a circuit board where auxiliary circuit boards can be plugged in. They are usually much longer than they are wide, and have a gap (i.e. Slot) running along the length. In software, ports are numbers used to identify the type of internet communication and the program that is designed to process that type. They are very old type of LOGIC BOARD which has 12 pins connectors,ram slots expansions slots (ISA) Used old model processor with LIF (Low Insertion force). For use of more features expansion slots are available for add-ons cards and some ports are available for additional features. They are typically slot type processor. In computing, an expansion card, also known as an expansion board, adapter card or accessory card, is a printed circuit board that can be inserted into an electrical connector, or expansion slot, on a computer motherboard, backplane or riser card to add functionality to a computer system via the expansion bus. A slot port vs sqaure port is the same thing, the only difference is the slot is Square ( all sides being equal ) vs slot rectangle ( unequal ) plus it has nothing to do with whether the walls of the enclosure are or are not used.